Difference between revisions of "ObjectsAndRefs"
From Hashphp.org
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
The above code creates a new class, SimpleClass, with no properties or methods. | The above code creates a new class, SimpleClass, with no properties or methods. | ||
It then creates a new instance of this class and attaches it to the variable | It then creates a new instance of this class and attaches it to the variable | ||
| − | named '$instance'. Because objects are "special" <ref>[http://blog.golemon.com/2007/01/youre-being-lied-to.html]</ref> in PHP5, | + | named '$instance'. Because objects are "special" <ref>Sara Golemon, "You're Being Lied To" [http://blog.golemon.com/2007/01/youre-being-lied-to.html]</ref> in PHP5, |
the relationship between the variable '$instance' and the object inside it is | the relationship between the variable '$instance' and the object inside it is | ||
not as direct as you might be expecting... | not as direct as you might be expecting... | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 26 July 2011
This page attempts to provide a visual guide to how objects - and references to them - work in PHP 5.0 and later.
| class SimpleClass { } $instance = new SimpleClass(); |
 |
The above code creates a new class, SimpleClass, with no properties or methods.
It then creates a new instance of this class and attaches it to the variable
named '$instance'. Because objects are "special" [1] in PHP5,
the relationship between the variable '$instance' and the object inside it is
not as direct as you might be expecting...
| |
| $assigned = $instance; |  |
| Explain the code here | |
| $instance->var = '$assigned will have this value as well'; |  |
| Explain the code here | |
| $reference =& $instance; | 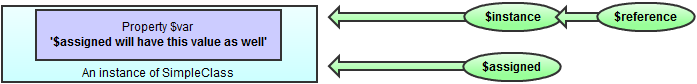 |
| Explain the code here | |
| $instance = null; | 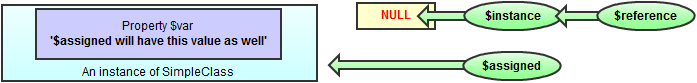 |
| Explain the code here | |